| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
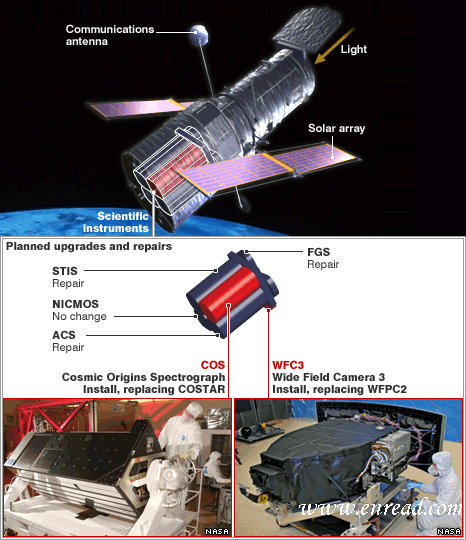
An inspection1 of the space shuttle Atlantis has uncovered some "minor2" damage to the vehicle's right side, Nasa officials say. NasaЙйдБГЦЃЌвЛЯюЖдАЂЬиРМЕйЫЙКХКНЬьЗЩЛњЕФМьВщжаЗЂЯжгввэгавЛаЉ“аЁУЋВЁ”ЁЃ Atlantis appears to be in good overall shape, but Nasa engineers in Houston are still studying the 53cm (21in) line of chips on the shuttle's right side. More analysis is required to evaluate the case for another inspection. Atlantis was launched on Monday to begin a risky3 repair mission intended to save the strickenЃЈЪмЩЫЕФЃЌЪмЧжЯЎЕФЃЉ space observatory4. Hubble has been hit by failures to its science instruments and to gyroscopesЃЈЭгТнвЧЃЌЛизЊвЧЃЉ. These gyros are used to point the observatory at targets in the sky. If successful, the mission could extend Hubble's lifetime beyond 2014. During their first full day in orbit, Atlantis's crew used a laser-tipped boom to look for any damage to the orbiter in a 10-hour inspection. The line of chips uncovered by the astronauts are in thick tiles that make up the protective heat shield on Atlantis' starboard sideЃЈгвЯЯЃЉ. The damage is located where the right wing joins the shuttle's fuselageЃЈЛњЩэЃЉ. Nasa said the chips could be related to a "debris5 event" detected by the wing's leading edge sensors6 104-106 seconds into the lift-off. Officials said the damage did not appear to be serious: "To my untrained eye... I would think [the chips] were minor," lead flight director Tony Ceccaci told reporters at a news conference in Houston. But more analysis by engineers would determine whether a "focused inspection" was needed in that specific area. If so, astronauts would use sensors to determine the exact depth of the damage to the heat shield tiles. Nasa has placed the space shuttle Endeavour on stand-by to rescue the crew of Atlantis if they are endangered. If something goes wrong on this mission, Atlantis's astronauts will not be able to shelter on the International Space Station (ISS). The station orbits at around 350km (220 miles) above Earth, while Hubble occupies an orbit about 560km (350 miles) up. Impacts from micrometeoroidsЃЈЮЂдЩаЧЬхЃЉ and space debris present one of the most perniciousЃЈгаКІЕФЃЌжТУќЕФЃЉ threats to the astronauts. There is more space junk - from old satellites and rocket stages - at Hubble's altitudeЃЈКЃАЮЃЌИпЖШЃЉ than at the ISS's. But a successful mission would make Hubble up to 90 times more powerful than it was in its original guise7ЃЈЭтЙлЃЉ. Atlantis roared up into the sky at 1901 BST (1401 EDT) on Monday from Florida's Kennedy Space Center. Nasa discovered a surprising amount of damage from Monday's launch at the pad used by Atlantis. Managers wanted to make sure none of the material blasted off during launch hit Atlantis. Atlantis is due to rendezvous8ЃЈдМЛсЃЌдМЛсЕиЕуЃЉ with Hubble just after 1700 BST (1200 EDT) on Wednesday. ЕуЛї  ЪеЬ§ЕЅДЪЗЂвє ЪеЬ§ЕЅДЪЗЂвє
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- ЗЂБэЦРТл
-
- зюаТЦРТл НјШыЯъЯИЦРТлвГ>>